New Page
Architecture de Foreman - Composants et Flux
Table des matières
- Vue d'ensemble de Foreman
- Les composants principaux
- Architecture détaillée
- Flux de communication
- Connexion des agents Puppet
- Architecture avec HAProxy
- Ports et protocoles
Vue d'ensemble de Foreman
Foreman est une plateforme complète de gestion du cycle de vie des serveurs. C'est bien plus qu'un simple outil de gestion de configuration : c'est une solution intégrée qui combine plusieurs technologies pour offrir un système complet d'orchestration et de provisioning.
Qu'est-ce que Foreman ?
Foreman permet de :
- Provisionner des serveurs physiques et virtuels (bare-metal et cloud)
- Configurer les systèmes via Puppet, Ansible, Salt ou Chef
- Gérer le cycle de vie complet des machines (de l'installation à la destruction)
- Monitorer l'état de configuration et les rapports
- Automatiser les tâches répétitives d'infrastructure
Philosophie d'architecture
Foreman suit une architecture modulaire où chaque composant a un rôle spécifique :
- Foreman Core : Interface web et logique métier
- Smart Proxy : Agent de communication avec l'infrastructure
- Puppet Server : Gestion de configuration
- Base de données : Stockage des données
- Services d'infrastructure : DNS, DHCP, TFTP
Architecture détaillée
Schéma d'architecture complète
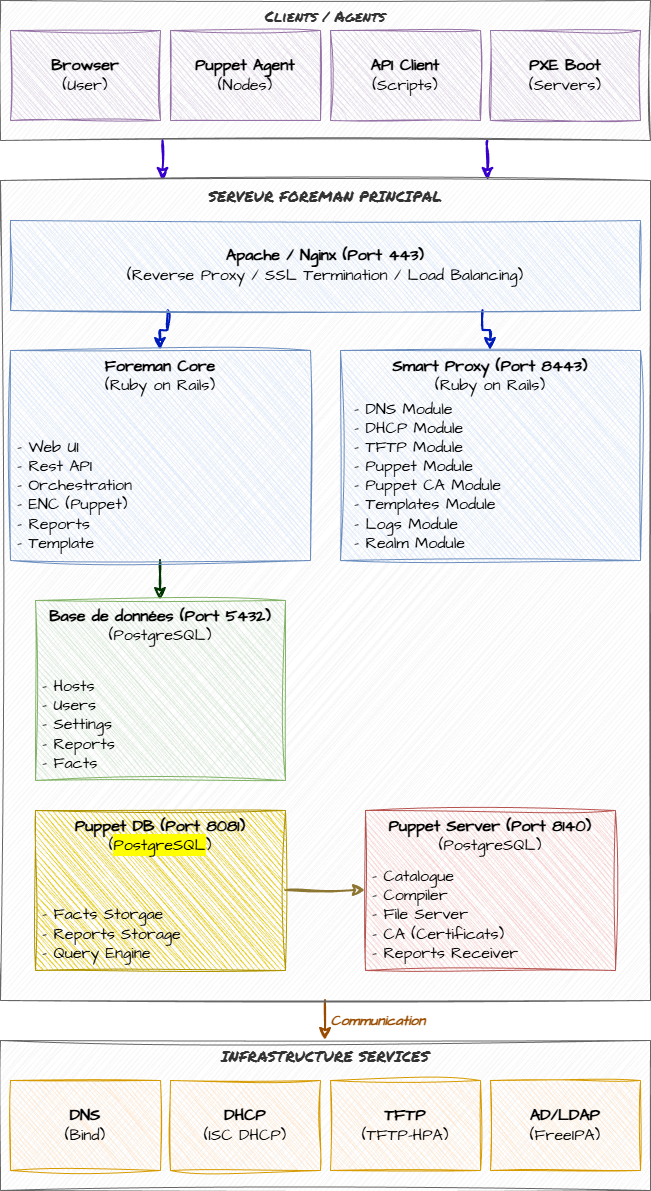
Les principaux composants
1. Foreman Core (Application Rails)
Rôle : Cerveau du système, interface web centrale
Caractéristiques :
- Application Ruby on Rails
- Interface web responsive
- API REST complète
- Gestion des utilisateurs et permissions (RBAC)
- Orchestration des autres composants
Fonctionnalités :
- Gestion des hôtes (inventaire)
- Templates de provisioning
- Gestion des paramètres et variables
- Rapports et monitoring
- Gestion des rôles et permissions
- Intégration avec les fournisseurs cloud (AWS, Azure, GCP, etc.)
Processus :
Service : foreman.service (Puma/Passenger)
Port : Aucun (accès via Apache/Nginx)
Utilisateur : foreman2. Apache/Nginx (Serveur Web)
Rôle : Serveur web frontal pour Foreman
Caractéristiques :
- Proxy inverse pour l'application Foreman
- Terminaison SSL/TLS
- Authentification (optionnel)
- Compression et cache
Configuration par défaut :
Port HTTP : 80 (redirigé vers HTTPS)
Port HTTPS : 443
Serveur backend : Puma (socket Unix)VirtualHosts principaux :
/: Application Foreman/pulp: Gestion de contenu (si activé)/pub: Fichiers publics (kickstart, preseed, etc.)
3. Smart Proxy (foreman-proxy)
Rôle : Agent d'infrastructure, bras armé de Foreman
Le Smart Proxy est le composant qui permet à Foreman d'interagir avec l'infrastructure réseau et les services. Il peut être installé sur le même serveur que Foreman ou sur des serveurs distants.
Fonctionnalités modulaires :
DNS
- Gestion des enregistrements DNS
- Création/suppression automatique d'entrées A, PTR, AAAA
- Support de BIND, PowerDNS, Route53, etc.
- Mode API ou nsupdate
DHCP
- Attribution d'adresses IP
- Création de réservations
- Support ISC DHCP, MS DHCP, Infoblox
- Gestion des options DHCP (next-server, filename, etc.)
TFTP
- Distribution des fichiers de boot PXE
- Templates de boot (pxelinux, grub2, iPXE)
- Gestion automatique des fichiers
Puppet CA
- Gestion des certificats Puppet
- Signature automatique ou manuelle
- Révocation de certificats
- Liste des certificats en attente
Puppet
- Déclenchement de runs Puppet
- Import de classes et environnements
- Récupération de facts
- Gestion des environnements
Templates
- Proxy pour les templates de provisioning
- Distribution des kickstart/preseed/cloud-init
- Génération à la volée
Logs
- Récupération de logs systèmes
- Agrégation des logs de boot
- Debugging du provisioning
Realm (Kerberos/AD)
- Intégration Active Directory
- Intégration FreeIPA
- Jointure automatique au domaine
Configuration :
Port : 8443 (HTTPS)
Protocole : REST API
Authentification : Certificat SSL client
Configuration : /etc/foreman-proxy/settings.yml
Modules : /etc/foreman-proxy/settings.d/*.yml
4. Puppet Server
Rôle : Serveur de gestion de configuration
Le Puppet Server est le composant central pour la gestion de configuration. Il stocke les manifests, modules et données, et les distribue aux agents.
Composants Puppet :
Puppet Server (JVM)
- Compile les catalogues
- Sert les fichiers et modules
- Gère les certificats (CA)
- Collecte les rapports
PuppetDB (optionnel mais recommandé)
- Base de données des facts
- Historique des catalogues
- Stockage des rapports
- Requêtes PQL (Puppet Query Language)
Puppet CA
- Autorité de certification
- Génération des certificats clients/serveurs
- Gestion du CRL (Certificate Revocation List)
Ports et services :
Puppet Server : 8140 (HTTPS)
PuppetDB : 8081 (HTTP/HTTPS)
Catalogue Compiler : Intégré dans 8140
Workflow Puppet :
1. Agent demande un certificat → Puppet CA
2. Agent envoie ses facts → Puppet Server
3. Server compile le catalogue → Renvoie à l'agent
4. Agent applique le catalogue
5. Agent renvoie le rapport → Puppet Server → PuppetDB
6. Foreman récupère le rapport → Affichage dans l'UI
5. Base de données
Rôle : Stockage persistant des données Foreman
Base de données supportées :
- PostgreSQL (recommandé en production)
- MySQL/MariaDB (supporté)
- SQLite (développement uniquement)
Données stockées :
- Inventaire des hôtes
- Configuration des hôtes
- Utilisateurs et permissions
- Paramètres et variables
- Templates
- Rapports Puppet (si PuppetDB non utilisé)
- Logs et audits
Configuration :
Base de données : foreman
Utilisateur : foreman
Port : 5432 (PostgreSQL) / 3306 (MySQL)
6. Services d'infrastructure (optionnels)
DNS (BIND, PowerDNS, etc.)
- Résolution de noms
- Zones directes et inverses
- Mises à jour dynamiques (DDNS)
DHCP (ISC DHCP, etc.)
- Attribution d'adresses IP
- Options PXE boot
- Réservations
TFTP
- Boot PXE
- Distribution des images de boot
- Chainloading (pxelinux, grub, iPXE)
Architecture détaillée
Schéma d'architecture complète
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ CLIENTS / AGENTS │
│ ┌──────────────┐ ┌──────────────┐ ┌──────────────┐ ┌──────────────┐ │
│ │ Browser │ │ Puppet Agent │ │ API Client │ │ PXE Boot │ │
│ │ (User) │ │ (Nodes) │ │ (Scripts) │ │ (Servers) │ │
│ └──────┬───────┘ └──────┬───────┘ └──────┬───────┘ └──────┬───────┘ │
└─────────┼──────────────────┼──────────────────┼──────────────────┼──────────┘
│ │ │ │
│ HTTPS (443) │ HTTPS (8140) │ HTTPS (443) │ TFTP/PXE
│ │ │ │ DHCP
▼ ▼ ▼ ▼
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ SERVEUR FOREMAN PRINCIPAL │
│ ┌──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ APACHE / NGINX (Port 443) │ │
│ │ - Reverse Proxy │ │
│ │ - SSL Termination │ │
│ │ - Load Balancing (optionnel) │ │
│ └────────┬──────────────────────────────────────┬────────────────────────┘ │
│ │ │ │
│ ▼ ▼ │
│ ┌────────────────────┐ ┌──────────────────────┐ │
│ │ FOREMAN CORE │◄────────────►│ FOREMAN PROXY │ │
│ │ (Ruby on Rails) │ │ (Port 8443) │ │
│ │ │ │ │ │
│ │ - Web UI │ │ - DNS Module │ │
│ │ - REST API │ │ - DHCP Module │ │
│ │ - Orchestration │ │ - TFTP Module │ │
│ │ - ENC (Puppet) │ │ - Puppet Module │ │
│ │ - Reports │ │ - Puppet CA Module │ │
│ │ - Templates │ │ - Templates Module │ │
│ └─────────┬──────────┘ │ - Logs Module │ │
│ │ │ - Realm Module │ │
│ │ └──────────┬───────────┘ │
│ ▼ │ │
│ ┌─────────────────────┐ │ │
│ │ BASE DE DONNÉES │ │ │
│ │ (PostgreSQL) │ │ │
│ │ │ │ │
│ │ - Hosts │ │ │
│ │ - Users │ │ │
│ │ - Settings │ │ │
│ │ - Reports │ │ │
│ │ - Facts │ │ │
│ └─────────────────────┘ │ │
│ │ │
│ ┌────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ │ │
│ ▼ │
│ ┌─────────────────────┐ ┌──────────────────────┐ │
│ │ PUPPET SERVER │ │ PUPPETDB │ │
│ │ (Port 8140) │◄────────────►│ (Port 8081) │ │
│ │ │ │ │ │
│ │ - Catalogue │ │ - Facts Storage │ │
│ │ - Compiler │ │ - Reports Storage │ │
│ │ - File Server │ │ - Query Engine │ │
│ │ - CA (Certificats) │ │ │ │
│ │ - Reports Receiver │ │ │ │
│ └─────────────────────┘ └──────────────────────┘ │
│ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
│
│ Communication
▼
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ INFRASTRUCTURE SERVICES │
│ ┌──────────────┐ ┌──────────────┐ ┌──────────────┐ ┌──────────────┐ │
│ │ DNS │ │ DHCP │ │ TFTP │ │ AD/LDAP │ │
│ │ (BIND) │ │ (ISC DHCP) │ │ (tftp-hpa) │ │ (FreeIPA) │ │
│ │ Port 53 │ │ Port 67 │ │ Port 69 │ │ Port 389 │ │
│ └──────────────┘ └──────────────┘ └──────────────┘ └──────────────┘ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
Flux de communication
1. Flux d'accès à l'interface web
┌─────────┐ ┌─────────────────┐
│ │ 1. HTTPS Request (443) │ │
│ Browser │───────────────────────────────────►│ Apache/Nginx │
│ │ │ (Reverse Proxy)│
└─────────┘ └────────┬────────┘
▲ │
│ │ 2. Forward to
│ │ Puma/Passenger
│ ▼
│ ┌─────────────────┐
│ 4. HTML Response │ Foreman Core │
│◄────────────────────────────────────────│ (Rails App) │
└────────┬────────┘
│
│ 3. DB Query
▼
┌─────────────────┐
│ PostgreSQL │
│ (Database) │
└─────────────────┘
Étapes détaillées :
- L'utilisateur accède à
https://foreman.mondomaine.com - Apache/Nginx reçoit la requête HTTPS
- Apache/Nginx forward la requête à Foreman via Puma/Passenger (socket Unix ou TCP)
- Foreman traite la requête (authentification, autorisation)
- Foreman interroge la base de données
- Foreman génère la réponse HTML
- Apache/Nginx renvoie la réponse au navigateur
2. Flux de provisioning d'un nouveau serveur
┌────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ PHASE 1 : Boot Initial │
└────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
Nouveau Serveur DHCP Smart Proxy Foreman
│ │ │ │
│ 1. DHCP Discover (PXE) │ │ │
├─────────────────────────►│ │ │
│ │ │ │
│ 2. DHCP Offer │ │ │
│ (IP + next-server) │ │ │
│◄─────────────────────────┤ │ │
│ │ │ │
│ 3. TFTP Request │ │ │
│ (pxelinux.0) │ │ │
├───────────────────────────────────────────────────► │
│ │ │ │
│ 4. Send bootloader │ │ │
│◄─────────────────────────────────────────────────── │
│ │ │ │
│ 5. Request PXE config │ │ │
│ (MAC address) │ │ │
├───────────────────────────────────────────────────► │
│ │ │ │
│ │ │ 6. Request PXE │
│ │ │ template │
│ │ ├──────────────────►│
│ │ │ │
│ │ │ 7. Generate │
│ │ │ template │
│ │ │◄──────────────────┤
│ │ │ │
│ 8. Send PXE config │ │ │
│ (kernel, initrd, params) │ │
│◄─────────────────────────────────────────────────── │
│ │ │ │
┌────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ PHASE 2 : Installation OS │
└────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
│ 9. Download kernel │ │ │
│ & initrd via TFTP │ │ │
├───────────────────────────────────────────────────► │
│◄─────────────────────────────────────────────────── │
│ │ │ │
│ 10. Boot installer │ │ │
│ (Anaconda/Debian │ │ │
│ Installer) │ │ │
│ │ │ │
│ 11. Request kickstart/preseed │ │
│ via HTTP/HTTPS │ │ │
├──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────►│
│ │ │ │
│ 12. Generate template │ │ │
│ (partitioning, │ │ │
│ packages, post) │ │ │
│◄──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ │ │ │
│ 13. Install OS │ │ │
│ (automated) │ │ │
│ │ │ │
│ 14. Post-install script │ │ │
│ - Install Puppet │ │ │
│ - Register to Foreman│ │ │
│ - Notify completion │ │ │
├──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────►│
│ │ │ │
┌────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ PHASE 3 : Configuration initiale Puppet │
└────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
│ │ │ │
│ 15. Request certificate │ │ │
│ to Puppet CA │ │ │
├───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ │ │ │
│ │ │ ▼ │
│ │ │ ┌──────────────┐
│ │ │ │ Puppet Server│
│ │ │ │ (CA) │
│ │ │ └──────┬───────┘
│ │ │ │ │
│ │ │ 16. Auto-sign │ │
│ │ │ (if enabled)│ │
│ │ │◄───────────────┘ │
│ │ │ │
│ 17. Certificate signed │ │ │
│◄───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ │ │ │
│ 18. First Puppet run │ │ │
│ (apply configuration)│ │ │
├───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ │ │ │
│ 19. Send report │ │ │ │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────►│
│ │ │ │
Résumé du provisioning :
- PXE Boot : Le serveur boot via réseau (DHCP + TFTP)
- PXE Config : Foreman génère un template PXE personnalisé
- Boot Installer : Le serveur charge kernel/initrd et démarre l'installateur
- Kickstart/Preseed : L'installateur récupère les instructions depuis Foreman
- Installation : L'OS s'installe automatiquement selon le template
- Post-installation : Scripts d'installation de Puppet et enregistrement
- Configuration : Premier run Puppet pour appliquer la configuration
3. Flux de gestion DNS/DHCP lors du provisioning
Foreman UI Foreman Core Smart Proxy DNS/DHCP
│ │ │ │
│ 1. Create new host │ │ │
│ (avec IP et MAC) │ │ │
├─────────────────────────►│ │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ 2. Orchestrate │ │
│ │ DNS creation │ │
│ ├──────────────────────►│ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ │ 3. Create A record │
│ │ │ (hostname → IP) │
│ │ ├──────────────────────►│
│ │ │ │
│ │ │ 4. Create PTR record │
│ │ │ (IP → hostname) │
│ │ ├──────────────────────►│
│ │ │ │
│ │ │ 5. Confirm creation │
│ │ │◄──────────────────────┤
│ │ │ │
│ │ 6. Orchestrate │ │
│ │ DHCP reservation │ │
│ ├──────────────────────►│ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ │ 7. Create reservation │
│ │ │ (MAC → IP) │
│ │ ├──────────────────────►│
│ │ │ │
│ │ │ 8. Add PXE boot opts │
│ │ │ (filename, next-srv)│
│ │ ├──────────────────────►│
│ │ │ │
│ │ │ 9. Confirm creation │
│ │ │◄──────────────────────┤
│ │ │ │
│ │ 10. Confirm to UI │ │
│◄─────────────────────────┤ │ │
│ │ │ │
Orchestration Foreman : Lorsqu'un hôte est créé/modifié/supprimé dans Foreman, celui-ci peut automatiquement :
- Créer/modifier/supprimer les enregistrements DNS (A, PTR, AAAA)
- Créer/modifier/supprimer les réservations DHCP
- Créer/modifier/supprimer les configurations PXE (TFTP)
- Créer/modifier/supprimer les entrées dans Active Directory/FreeIPA
Connexion des agents Puppet
Architecture de connexion Puppet
┌────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Agent Puppet (Client) │
│ ┌──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ 1. Puppet Agent Service │ │
│ │ - puppet agent --test (manuel) │ │
│ │ - Service en arrière-plan (toutes les 30min par défaut) │ │
│ │ - Déclenchement via API (depuis Foreman) │ │
│ └──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ │ │
│ │ puppet.conf : │
│ │ server = foreman.mondomaine.com │
│ │ ca_server = foreman.mondomaine.com │
│ │ certname = client1.mondomaine.com │
│ │ │
└──────────────────────────────────┼──────────────────────────────────────┘
│
│ HTTPS (8140)
│ mTLS (mutual TLS)
│
▼
┌────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Serveur Foreman / Puppet Server │
│ ┌──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ Puppet Server (Port 8140) │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ ┌────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │ │
│ │ │ 2. Puppet CA (Certificate Authority) │ │ │
│ │ │ - Génération des certificats clients │ │ │
│ │ │ - Signature des certificats (auto ou manuelle) │ │ │
│ │ │ - Validation mTLS │ │ │
│ │ └────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │ │
│ │ │ │ │
│ │ ▼ │ │
│ │ ┌────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │ │
│ │ │ 3. Catalogue Compiler │ │ │
│ │ │ - Reçoit les facts de l'agent │ │ │
│ │ │ - Demande l'ENC à Foreman │ │ │
│ │ │ - Compile le catalogue Puppet │ │ │
│ │ │ - Renvoie le catalogue à l'agent │ │ │
│ │ └────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │ │
│ │ │ │ │
│ │ ▼ │ │
│ │ ┌────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │ │
│ │ │ 4. Reports Receiver │ │ │
│ │ │ - Reçoit les rapports post-run de l'agent │ │ │
│ │ │ - Stocke dans PuppetDB │ │ │
│ │ │ - Notifie Foreman │ │ │
│ │ └────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │ │
│ └──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ │ │
│ │ │
│ ┌────────────────────────┼────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ │ │ │
│ ▼ ▼ ▼ │
│ ┌─────────────┐ ┌─────────────┐ ┌─────────────┐ │
│ │ Foreman │ │ PuppetDB │ │ Environments│ │
│ │ (ENC) │ │ (Facts & │ │ & Modules │ │
│ │ │ │ Reports) │ │ │ │
│ │ - Classes │ │ │ │ - manifests │ │
│ │ - Params │ │ │ │ - modules │ │
│ │ - Variables │ │ │ │ - data │ │
│ └─────────────┘ └─────────────┘ └─────────────┘ │
└────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
Cycle de vie d'un agent Puppet - Détaillé
Phase 1 : Enregistrement initial (première fois)
Agent Puppet Puppet CA Foreman
│ │ │
│ 1. Generate CSR │ │
│ (Certificate Signing │ │
│ Request) │ │
├─────────────────────────────►│ │
│ │ │
│ │ 2. Validate CSR │
│ │ (CN, DNS alt names) │
│ │ │
│ │ 3. Wait for signature │
│ │ (ou auto-sign si activé)│
│ │ │
│ [ADMIN ACTION] │ │
│ Sur le serveur Foreman : │ │
│ puppetserver ca sign --certname client1.mondomaine.com │
│ │ │
│ │ 4. Certificate signed │
│ │ │
│ 5. Download certificate │ │
│◄─────────────────────────────┤ │
│ │ │
│ 6. Store locally │ │
│ /etc/puppetlabs/ │ │
│ puppet/ssl/ │ │
│ │ │
Fichiers de certificats sur l'agent :
/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/
├── ca/
│ └── ca_crt.pem # Certificat de la CA
├── certificate_requests/
│ └── client1.mondomaine.com.pem # CSR (si non signé)
├── certs/
│ └── client1.mondomaine.com.pem # Certificat client signé
└── private_keys/
└── client1.mondomaine.com.pem # Clé privée client
Phase 2 : Run Puppet (normal)
Agent Puppet Server Foreman (ENC) PuppetDB
│ │ │ │
│ 1. Collect Facts │ │ │
│ (facter) │ │ │
│ - OS, IP, RAM, etc. │ │ │
│ │ │ │
│ 2. Connect via mTLS │ │ │
│ (certificat client) │ │ │
├────────────────────────►│ │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ 3. Request node data │ │
│ │ from ENC │ │
│ ├────────────────────────►│ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ 4. Return: │ │
│ │ - Classes to apply │ │
│ │ - Parameters │ │
│ │ - Environment │ │
│ │◄────────────────────────┤ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ 5. Compile catalogue │ │
│ │ (manifests + facts │ │
│ │ + ENC data) │ │
│ │ │ │
│ 6. Send catalogue │ │ │
│ (JSON format) │ │ │
│◄────────────────────────┤ │ │
│ │ │ │
│ 7. Apply catalogue │ │ │
│ (make changes) │ │ │
│ - Install packages │ │ │
│ - Configure files │ │ │
│ - Manage services │ │ │
│ │ │ │
│ 8. Generate report │ │ │
│ - Success/failures │ │ │
│ - Changed resources │ │ │
│ - Metrics │ │ │
│ - Logs │ │ │
├────────────────────────►│ │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ 9. Store report │ │
│ ├─────────────────────────────────────────►│
│ │ │ │
│ │ 10. Notify Foreman │ │
│ ├────────────────────────►│ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ │ 11. Update UI │
│ │ │ - Last run │
│ │ │ - Status │
│ │ │ - Metrics │
│ │ │ │
Détail du catalogue Puppet :
Le catalogue est un document JSON qui décrit l'état souhaité de la machine :
{
"resources": [
{
"type": "Package",
"title": "httpd",
"parameters": {
"ensure": "installed"
}
},
{
"type": "Service",
"title": "httpd",
"parameters": {
"ensure": "running",
"enable": true
}
},
{
"type": "File",
"title": "/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf",
"parameters": {
"ensure": "file",
"content": "...",
"mode": "0644"
}
}
]
}
Phase 3 : Intégration Foreman comme ENC (External Node Classifier)
Foreman agit comme un ENC pour Puppet Server. Voici comment cela fonctionne :
Configuration Puppet Server (/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/puppet.conf) :
[master]
node_terminus = exec
external_nodes = /etc/puppetlabs/puppet/node.rb
Script ENC (/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/node.rb) :
#!/usr/bin/env ruby
# Ce script appelle l'API Foreman pour récupérer les informations du nœud
require 'net/http'
require 'yaml'
# URL de l'API Foreman
foreman_url = "https://foreman.mondomaine.com/api/v2/hosts/#{ARGV[0]}"
# Appel API
response = Net::HTTP.get_response(URI(foreman_url))
data = JSON.parse(response.body)
# Retourne en format YAML pour Puppet
output = {
'classes' => data['puppetclasses'],
'parameters' => data['parameters'],
'environment' => data['environment']
}
puts output.to_yaml
Réponse de l'ENC (format YAML) :
---
classes:
- apache
- mysql
- php
parameters:
apache_port: 8080
mysql_root_password: secret
environment: production
environment: production
Déclenchement des runs Puppet
Il existe plusieurs façons de déclencher un run Puppet :
1. Run automatique (service)
L'agent Puppet tourne en arrière-plan et exécute un run périodiquement :
# Configuration dans /etc/puppetlabs/puppet/puppet.conf
[agent]
runinterval = 1800 # 30 minutes par défaut
Le service :
sudo systemctl enable puppet
sudo systemctl start puppet
# Le service exécutera puppet agent --onetime toutes les 30 minutes
2. Run manuel
# Run complet avec verbose
sudo /opt/puppetlabs/bin/puppet agent --test
# Run en mode dry-run (simulation)
sudo /opt/puppetlabs/bin/puppet agent --test --noop
# Run en arrière-plan
sudo /opt/puppetlabs/bin/puppet agent --onetime --no-daemonize
3. Déclenchement depuis Foreman
Foreman peut déclencher un run sur un ou plusieurs agents via l'API du Smart Proxy :
Via l'interface Web :
Hosts → All Hosts → Sélectionner un host → Run Puppet
Via l'API Foreman :
curl -X POST https://foreman.mondomaine.com/api/v2/hosts/client1.mondomaine.com/puppetrun \
-u admin:password \
-H "Content-Type: application/json"
Flux du déclenchement distant :
Foreman UI/API → Smart Proxy → SSH/MCO/Salt vers l'agent → puppet agent --onetime
4. Déclenchement via MCollective ou Salt (optionnel)
Si configuré, Foreman peut utiliser MCollective ou Salt pour déclencher des runs :
# Via MCollective
mco puppet runonce -I client1.mondomaine.com
# Via Salt
salt 'client1.mondomaine.com' puppet.run
Architecture avec HAProxy
Lorsque HAProxy est ajouté comme reverse proxy, voici l'architecture modifiée :
┌────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ CLIENTS / AGENTS │
│ ┌──────────┐ ┌──────────┐ ┌──────────┐ ┌──────────┐ │
│ │ Browser │ │ Puppet │ │ API │ │ PXE │ │
│ │ (443) │ │ (8140) │ │ (443) │ │ (67/69) │ │
│ └────┬─────┘ └────┬─────┘ └────┬─────┘ └────┬─────┘ │
└───────┼─────────────┼─────────────┼─────────────┼─────────────────┘
│ │ │ │
│ HTTPS │ TCP/mTLS │ HTTPS │ DHCP/TFTP
│ │ │ │
▼ ▼ ▼ ▼
┌────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ SERVEUR HAPROXY (Frontend) │
│ ┌──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ Frontend Configuration │ │
│ │ ┌────────────┐ ┌────────────┐ ┌────────────┐ │ │
│ │ │ Port 443 │ │ Port 8140 │ │ Port 8443 │ │ │
│ │ │ (HTTPS) │ │ (TCP/TLS) │ │ (HTTPS) │ │ │
│ │ │ WebUI │ │ Puppet │ │ Proxy │ │ │
│ │ └──────┬─────┘ └──────┬─────┘ └──────┬─────┘ │ │
│ └─────────┼────────────────┼────────────────┼───────────────────┘ │
│ │ │ │ │
│ SSL │ TCP │ SSL │ │
│ Term │ Passthru │ Term │ │
│ │ │ │ │
└────────────┼────────────────┼────────────────┼──────────────────────┘
│ │ │
│ HTTP (80) │ TCP (8140) │ HTTPS (8443)
│ │ │
▼ ▼ ▼
┌────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ SERVEUR FOREMAN (Backend) │
│ ┌──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ Apache (Port 80) │ │
│ │ (HTTP - SSL terminated) │ │
│ └────────────────────────┬─────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ │ │
│ ▼ │
│ ┌─────────────────┐ │
│ │ Foreman Core │ │
│ │ (Rails App) │ │
│ └────────┬────────┘ │
│ │ │
│ ┌─────────────────┼─────────────────┐ │
│ │ │ │ │
│ ▼ ▼ ▼ │
│ ┌──────────────┐ ┌─────────────┐ ┌──────────────┐ │
│ │ Foreman │ │ Puppet │ │ PostgreSQL │ │
│ │ Proxy │ │ Server │ │ Database │ │
│ │ (8443) │ │ (8140) │ │ │ │
│ └──────┬───────┘ └──────┬──────┘ └──────────────┘ │
│ │ │ │
└─────────┼─────────────────┼─────────────────────────────────────────┘
│ │
▼ ▼
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Infrastructure Services │
│ ┌──────────┐ ┌──────────┐ ┌──────────┐ ┌──────────┐ │
│ │ DNS │ │ DHCP │ │ TFTP │ │ AD/LDAP │ │
│ └──────────┘ └──────────┘ └──────────┘ └──────────┘ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
Points clés avec HAProxy
-
WebUI (Port 443) :
- HAProxy : Terminaison SSL, forward en HTTP vers Foreman:80
- Headers X-Forwarded-* ajoutés pour conserver l'info client
-
Smart Proxy (Port 8443) :
- HAProxy : Terminaison SSL, forward en HTTPS vers Foreman:8443
- OU : Mode TCP passthrough (sans inspection SSL)
-
Puppet Server (Port 8140) :
- HAProxy : Mode TCP passthrough (mTLS de bout en bout)
- Pas de terminaison SSL (certificats clients Puppet)
- Forward direct vers Foreman:8140
-
Configuration Foreman :
- Trusted proxies : Ajouter IP HAProxy
- Apache RemoteIP : Récupérer la vraie IP client
Ports et protocoles
Tableau récapitulatif des ports
| Port | Protocole | Service | Direction | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 80 | HTTP | Apache/Nginx | Client → Server | WebUI (redirect vers 443) |
| 443 | HTTPS | Apache/Nginx | Client → Server | WebUI principale |
| 8140 | HTTPS | Puppet Server | Agent → Server | Catalogue, fichiers, rapports (mTLS) |
| 8443 | HTTPS | Smart Proxy | Foreman → Proxy | API Smart Proxy |
| 5432 | PostgreSQL | PostgreSQL | Foreman → DB | Base de données Foreman |
| 8081 | HTTP/HTTPS | PuppetDB | Puppet → PuppetDB | Stockage facts et rapports |
| 53 | DNS | BIND/PowerDNS | Client → DNS | Résolution DNS |
| 67 | DHCP | ISC DHCP | Client → DHCP | Attribution IP |
| 69 | TFTP | tftp-hpa | Client → TFTP | Boot PXE |
| 389 | LDAP | FreeIPA/AD | Foreman → LDAP | Authentification externe |
| 636 | LDAPS | FreeIPA/AD | Foreman → LDAP | Authentification externe (SSL) |
Avec HAProxy
| Port | Protocole | Frontend (HAProxy) | Backend (Foreman) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 80 | HTTP | Redirect → 443 | - | Force HTTPS |
| 443 | HTTPS | SSL Termination | HTTP:80 | WebUI |
| 8140 | TCP/mTLS | TCP Passthrough | TCP:8140 | Puppet (mTLS de bout en bout) |
| 8443 | HTTPS | SSL Termination | HTTPS:8443 | Smart Proxy API |
Résumé des flux
Flux principaux
-
Accès WebUI :
Browser → HAProxy:443 (HTTPS) → Foreman:80 (HTTP) → Rails App → PostgreSQL -
Agent Puppet - Catalogue :
Agent → HAProxy:8140 (mTLS) → Puppet:8140 → Foreman ENC → Compile → Agent -
Agent Puppet - Rapport :
Agent → Puppet:8140 → PuppetDB:8081 → Foreman (webhook/API) -
Provisioning PXE :
Server → DHCP → TFTP → Smart Proxy → Foreman (template) → Installer -
Orchestration DNS/DHCP :
Foreman → Smart Proxy:8443 → DNS/DHCP services
Sécurité des communications
- WebUI : HTTPS avec certificat SSL/TLS
- Smart Proxy : HTTPS avec authentification par certificat client
- Puppet : HTTPS avec mTLS (mutual TLS, certificats client et serveur)
- Database : Connexion locale ou SSL/TLS si distance
- PuppetDB : HTTPS avec certificat SSL
Conclusion
L'architecture de Foreman est modulaire et extensible :
- Foreman Core : Orchestrateur central et interface utilisateur
- Smart Proxy : Extension de Foreman vers l'infrastructure
- Puppet Server : Moteur de configuration
- Services d'infrastructure : DNS, DHCP, TFTP pour le provisioning
Les agents Puppet se connectent via mTLS sur le port 8140, récupèrent leur configuration depuis Foreman (via ENC), et appliquent les changements de manière déclarative.
L'ajout de HAProxy permet de centraliser les accès, gérer le SSL/TLS, et protéger le serveur Foreman des accès directs.
Cette architecture offre :
- Scalabilité : Smart Proxies distribués
- Sécurité : mTLS, RBAC, certificats
- Flexibilité : Plugins, API, intégrations multiples
- Automatisation : Provisioning complet de l'installation à la configuration
